NATURE
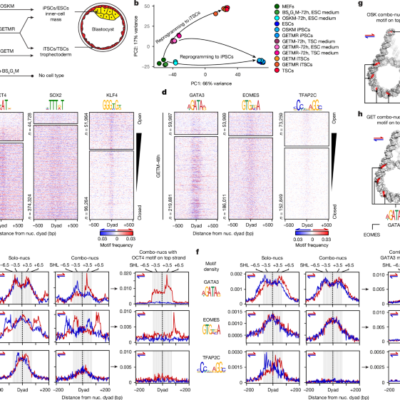
Nucleosome fibre topology guides transcription factor binding to enhancers
- By fromermedia@gmail.com
- . December 18, 2024
Inclusion and ethics All animal experiments for the iPS cell and iTS cell generation from MEFs were approved by the
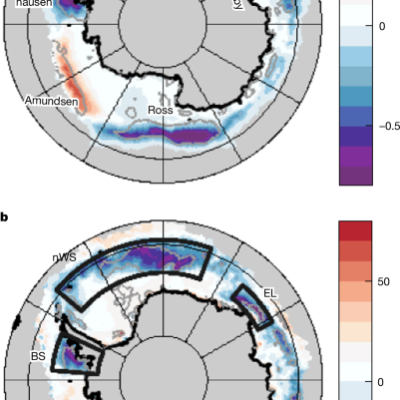
Record-low Antarctic sea ice in 2023 increased ocean heat loss and storms
- By fromermedia@gmail.com
- . December 18, 2024
Data sources The surface flux, meteorological variables and sea-ice concentration presented in our study are from the European Centre for
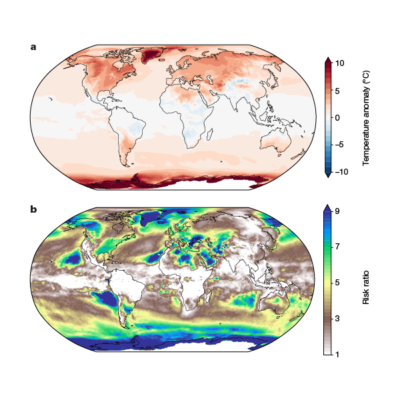
Atmospheric rivers lead to heat extremes
- By fromermedia@gmail.com
- . December 18, 2024
RESEARCH BRIEFINGS 18 December 2024 Atmospheric rivers are long, narrow bands of water vapour in the lower atmosphere that often
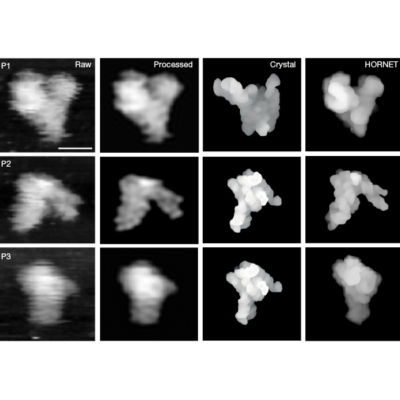

Machine learning helps to determine the diverse conformations of RNA molecules
- By fromermedia@gmail.com
- . December 18, 2024
RESEARCH BRIEFINGS 18 December 2024 An innovative technique called HORNET uses atomic force microscopy and a machine-learning architecture called a
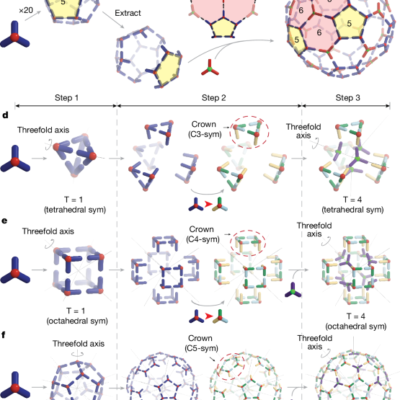
Four-component protein nanocages designed by programmed symmetry breaking
- By fromermedia@gmail.com
- . December 18, 2024
We generated base T = 1 tetrahedral, octahedral and icosahedral cages from the BGL17_A32 homotrimer using RPXdock20,21 to sample rotational and translational
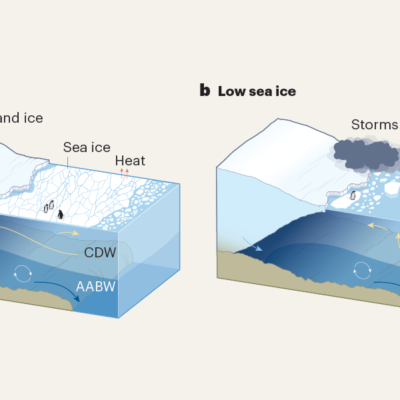
Sea ice is shrinking during Antarctic winter: here’s what it means for Earth’s oceans and atmosphere
- By fromermedia@gmail.com
- . December 18, 2024
Nature, Published online: 18 December 2024; doi:10.1038/d41586-024-04078-7 The extent of Antarctic sea ice dropped precipitously in 2023. Analysis shows that
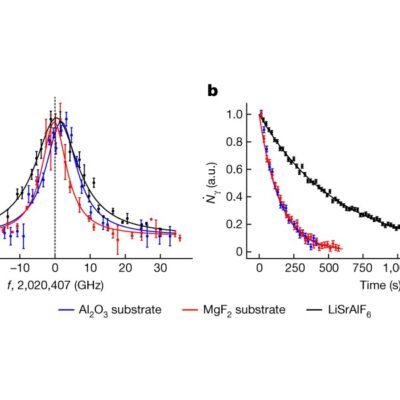
Vapour-deposited thin films raise the possibility of portable nuclear clocks
- By fromermedia@gmail.com
- . December 18, 2024
RESEARCH BRIEFINGS 18 December 2024 A rare isotope, thorium-229, exhibits a unique low-energy nuclear transition that could form the basis
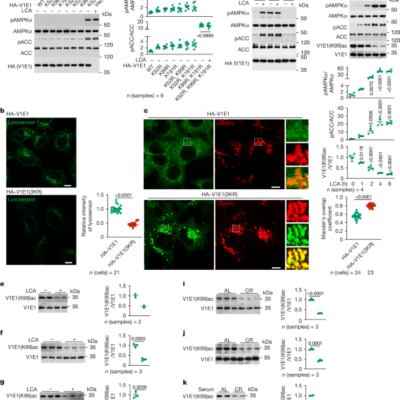
Lithocholic acid binds TULP3 to activate sirtuins and AMPK to slow down ageing
- By fromermedia@gmail.com
- . December 18, 2024
Data reporting The chosen sample sizes were similar to those used in this field: n = 4–5 samples were used to evaluate

Lithocholic acid phenocopies anti-ageing effects of calorie restriction
- By fromermedia@gmail.com
- . December 18, 2024
Data reporting The chosen sample sizes were similar to those used in the field: n = 4–12 samples were used to evaluate

Algae use the underwater light spectrum to sense depth
- By fromermedia@gmail.com
- . December 18, 2024
Nature, Published online: 18 December 2024; doi:10.1038/d41586-024-04079-6 Aquatic algae called diatoms have been found to use light-sensing proteins as depth
